
Flow Cytometry Tips
We are dedicated to helping our customers achieve exceptional results. While the information below can never be an exclusive solution to every problem you may encounter; it is our hope that you will find the information useful and even beneficial in troubleshooting any problems you may have. Of course, if you find you are still having problems you may submit them to us using this Flow Cytometry Troubleshooting Form.
SYMPTOMS
- No signal/weak fluorescence
- High fluorescence intensity
- Two cell populations
- High side scatter background
- Low event rate
- High event rate
- Unusual scatter profiles
- Unexpected staining
- Loss of epitope
- High background/high percentage of cells
- No events
No signal/weak fluorescence
Signal not correctly compensated |
Make sure everything is gated properly by checking the positive single color control and adjust compensation accordingly. |
Insufficient antibody |
Increase the antibody concentration to all experimental tubes. |
Intracellular target not available |
Check to see if the target protein is intracellular. If so, make sure to permeabilize on ice and with cold reagents in order to stop all reactions. |
Excess cell number |
Dilute sample tubes in PBS for recommended concentration |
Lasers not aligned |
Run setup beads and adjust alignment if necessary. |
Soluble/secreted target protein |
Target protein must be membrane bound or cytoplasmic to be detected. A Golgi-block step, such as Brefaldin A, may improve signal. |
Offset too high/gain too low |
Make sure your positive control has a peak at 102. Check fluorescent signal and adjust voltage (within reason). |
Primary and secondary are not compatible |
Secondary should be raised against the host species of the primary. |
PE antibody doesn't stain but FITC gives good results |
Paraformaldehyde can release methanol in its breakdown, which will affect the staining. |
Fluorochrome fluorescence faded |
Sample may have been left out too long or been exposed too long. Experiment should be repeated with fresh antibody. |
High fluorescence intensity
Antibody concentration |
Too much antibody will give high non-specific binding or very high intensity fluorescence. |
Excess antibody trapped |
Ensure adequate washing steps and include tween or triton in the wash buffers. Fluorochrome molecules can be trapped while staining intracellular. |
Inadequate blocking |
Dilute antibodies in blocking solution, and increase the blocking time. |
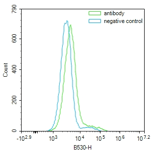
Two cell populations
More than one cell population present expressing target protein |
Lessen the This may be in part to debris or adequate cell separation. Check expected expression levels from cell types contained in the sample. |
Cell doublets present |
Cells can be filter or sieved to remove unnecessary clumps. Mix cells gently with a pipette before staining and again before acquiring. |
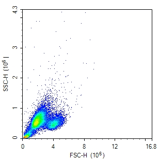
High side scatter background
Cells lysed |
Samples need to be fresh and prepared correctly. Do not vortex too violently, or centrifuge too fast. |
Bacterial contamination |
Bacterial will auto fluoresce at low level. This will give a high event rate |
Low event rate
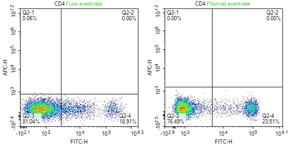
Low number of cells/ml |
Optimal cell concentration for each sample should be around 1x10^6 cells/ml. Ensure cells are gently mixed. |
Cells clumped/blocking tubing |
Pipette gently before staining and again before running. It's recommended to use to a filtered tube when running sample. |
High event rate
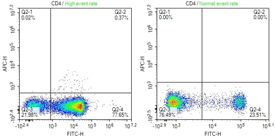
Protein load |
Use less protein and/or try an immunoprecipitation to enrich your target in the lysate. |
Antibody concentration |
Dilute the antibody concentration. |
Unusual scatter profiles
Showing dead cells |
This may be debris, and gates need to be adjusted. Or all cells could have died during mixing or additional chemicals added. Repeat experiment with fresh cells. |
Activation methods may affect scatter characteristics of cells |
This should be ok if the positive and negative control tubes were properly set up. Or if required, consult a different activation method. |
Unexpected staining
Presence of dead cells |
Always sieve the cells once before acquiring and sorting to remove any dead cell debris. Use freshly isolated cells as opposed to frozen cells whenever possible. |
Affect antigen detection |
Permeablization is required. However, reagents can affect certain antigens, i.e. lysis buffers and EDTA affects platelet markers. |
Loss of epitope
Too much paraformaldehyde |
Make sure to only use 1% paraformaldehyde. |
Sample fixed too long |
Follow proper instructions, most cells only need to be fix for less than 15 minutes. It is recommended to not fix for too long, as this will damage cells. |
Sample wasn't kept cold |
Follow proper protocol instructions, however most antibodies need to be kept at 4C to prevent loss of activity. Also, this prevents active phosphatases and proteases from altering the epitope of interest. |
High background/high percentage of cells
Gain set too high/offset too low |
Use the positive control to set up the flow cytometer correctly again, using the offset to reduce background from small particles and reduce the gain to decrease the signal. |
Excess antibody |
Decrease the antibody concentration. Detergent can also be added to the wash buffers to ensure any excess antibody is washed away. |
No events
Clogged sample tube |
Unclog flow cytometer injection tube as per instrument manufacturer's instructions (typically run 10% bleach for 5-10 min, followed by dH2O for 5-10 min). |